Third grade teacher Ms. Kim is really struggling with her student Aiden. Every day, he argues over simple things, seemingly just for the sake of causing trouble. He refuses to take responsibility for his behavior, even when caught in the act. And today, Aiden tore up a fellow student’s art project after that student wouldn’t let him use their red marker. His parents say he’s the same at home. A school counselor finally suggests that many of these behaviors line up with the symptoms of ODD in kids—oppositional defiant disorder.
What is ODD?
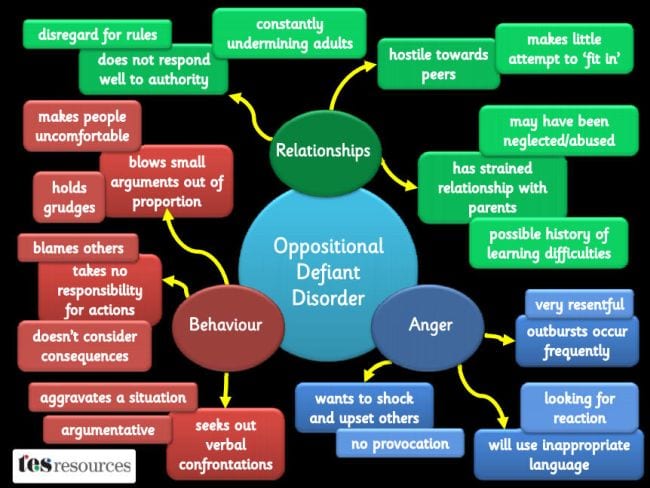
Image: TES Resources
Oppositional defiant disorder, commonly known as ODD, is a behavioral disorder in which children are—as the name suggests—defiant to the degree that it interferes with their daily lives. The DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, defines it as a pattern of angry, vindictive, argumentative, and defiant behavior that lasts at least six months.
In an article on Headteacher Update, Dr. Nicola Davies sums it up this way: “The goal of a student with oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is to gain and maintain control by testing authority to the limit, breaking rules, and provoking and prolonging arguments. In the classroom, this can be distracting for both the teacher and other students.”
Between 2% and 16% of the population may have ODD, and we’re not entirely sure of the causes. Scientists believe it could be genetic, environmental, biological, or a mix of all three. It’s diagnosed more often in younger boys than girls, though by their teen years, both seem to be equally affected. It co-occurs in many kids with ADHD, with some studies indicating up to 50% of students with ADHD also have ODD.
What does ODD in kids look like?
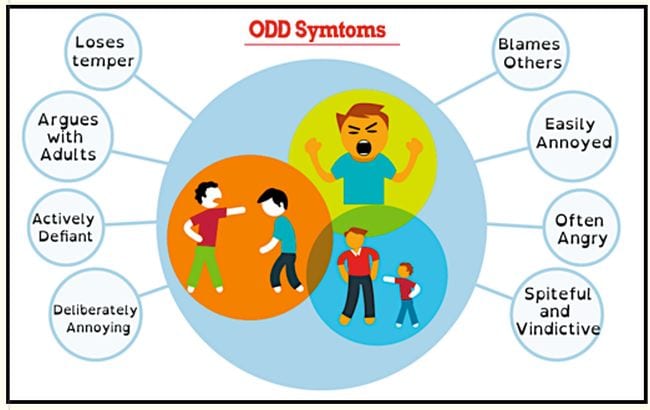
Image: ACOAS
We all know that kids of a certain age, especially toddlers and teenagers, are pretty much always arguing and defying. In fact, those can be appropriate behaviors at those ages, as kids test the world around them and learn how it works.
However, ODD is a whole lot more than that, to the point where students with ODD disrupt their own lives and often the lives of everyone around them. Kids with ODD push the limits of defiance far beyond reason. Their problem behavior is much more extreme than that of their peers, and it happens much more often.
Defiance and arguing
Most kids go through a phase where “no” is their favorite word, but for students with ODD, that phase never ends. They question everything, all the time, and consistently refuse to comply with rules and requests. Their need for argument may lead them to deliberately annoy others in an attempt to create conflict. However, they usually refuse to take responsibility for their mistakes or behaviors, blaming others for everything.
Anger and irritability
These are the kids who seem angry all the time and fly off the handle at the slightest provocation. Their overreactions may devolve into temper tantrums, not just occasionally but frequently. Therefore, every conversation you have with them seems to be a struggle.
Vindictiveness
The ongoing anger of kids with ODD can lead to vindictiveness and a need for revenge. They are spiteful and retaliatory, holding grudges and demanding punishment for others.
Not surprisingly, these behaviors cause students with ODD to struggle both at home and in school. It’s hard for them to make friends, and their schoolwork often suffers too. They may become depressed or anxious, or develop conduct or substance abuse disorders as they grow older. Early identification and treatment are vital to helping these kids.
How can teachers help kids with ODD?

It’s vital that teachers and parents work together to help students with ODD. The experienced teachers in the WeAreTeachers Helpline group on Facebook suggest trying these methods at school and at home. Find more ideas at Pathway 2 Success.
Be consistent
“Instead of arguing, repeat your words and consequences,” says Brandy T. “I use trigger words that I often repeat so the student knows I mean business. If a student tries to argue, I simply say either ‘not now,’ ‘later,’ or ‘fix the issue!’ The student then knows they can go to their chill-out space if they need to calm down.”
Give them space to reset
Kids with ODD can learn to recognize when they’re feeling overwhelmed and getting ready to challenge or defy. Giving them a safe space to calm down and rethink their choices can be beneficial. Calm-down corners have become popular in classrooms for this very reason. “Put out books, coloring, LEGO bricks, etc., in a place where they can go on their own when they feel like they need a break,” says Tobey G. “Often immediately after activities with a lot of stimulation, these kids need a safe space to calm down. Let them decide if and when they need to excuse themselves.”
Give them choices
Kids with ODD are looking for control. Rather than letting them drive the situation, you can give them a feeling of control while maintaining control yourself. “Always give choices,” advises Holli A. “State your choices—then walk away. Give the student time to process and decide which choice to make. If they don’t like the choices, don’t engage. When they try to argue, repeat the choices, and walk away again. If the student still will not choose, they do not get to participate in their preferred activity.”
As in other situations, it pays to stay consistent in your classroom rules and discipline. “After I give choices, I always reinforce the classroom rules and procedures and follow up with an appropriate consequence,” says Kristel R. “You cannot falter; stick to your rules and follow through.”
Offer positive reinforcement and appropriate rewards
Kids with ODD often respond to positive behavior reinforcement. It’s helpful to offer them a chance to earn certain privileges, rather than taking those privileges away as punishment. For instance, give them the ability to earn screen time when they promptly do as they’re asked, instead of threatening to take away screens when they defy.
When using a reward system, make sure that it is appropriate and isn’t perceived as manipulation. Leslie L. uses a behavior tracking system and a reward system where students can turn in points for an incentive (iPad time, lunch with a teacher, etc.). “I also build breaks right into their schedule,” adds Leslie. “And I try to be as patient and understanding as I possibly can.”
Teacher Erica M. also uses a point system checklist with options A and B. If they do each one, they earn “points” for an incentive, which often is iPad time during the last 15 minutes of class. “Find an interest and use that to your advantage!” Erica says.

Avoid power struggles
Most teachers agreed: Stay out of those winless power struggles. As Kris W. said, “Pick your battles. A student of mine corrects me all the time, whether I am wrong or not. I answer back, ‘OK, let’s double-check that.’ If I made a mistake, I correct it, and we move on; if he’s wrong, I silently let him figure it out.”
Make personal connections
Often kids with ODD are looking for a relationship with a teacher who can help them deal with problems on their own instead of making them stand out in a negative way. Building a connection with them will help get to the root of the behavior.
“Almost all of my students have ODD, and I have a great relationship with most of them,” says Kendra J. “Find out what they are interested in and have conversations on their level during breaks.” Allow them to set goals and decide together what the consequences will be if they don’t meet the goal.
Carol H. says, “Find something at the student’s interest level. I once had a middle school girl who hated all of her teachers and was out of control. She would curse at adults and peers, scratch, bite, and refuse to complete work. I found out she played soccer for a travel team. So did my son. A few weeks into the school year, she had a game adjacent to my son’s, and I was able to watch her play. It changed everything. She is a freshman in college now, and we still keep in touch.”
Find ODD Resources
This is just an overview of what students with ODD are facing. Educate yourself about the condition to find more ways to understand and help these kids in your classroom.
Online
- Mayo Clinic: Oppositional Defiant Order
- Childmind Institute: What Is Oppositional Defiant Order?
- Parenting for Brain: Oppositional Defiant Order Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
Books
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the book links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
- The Explosive Child: A New Approach for Understanding and Parenting Easily Frustrated, Chronically Inflexible Children (Greene, 2021)
- Overcoming Oppositional Defiant Disorder: A Two-Part Treatment Plan To Help Parents and Kids Work Together (Atencio-MacLean, 2019)
- The Parent’s Guide to Oppositional Defiant Disorder (Bowler, 2020)
- Parenting Children With Oppositional Defiant Disorder: A Modern Approach to Understand and Lead Your O.D.D. Child to Success (Bass, 2022)
Have more questions about kids with ODD? Come share your thoughts and ask for advice in the WeAreTeachers Helpline Facebook group.
Plus, check out 11 of the Biggest Classroom Management Mistakes (Plus How To Fix Them).


